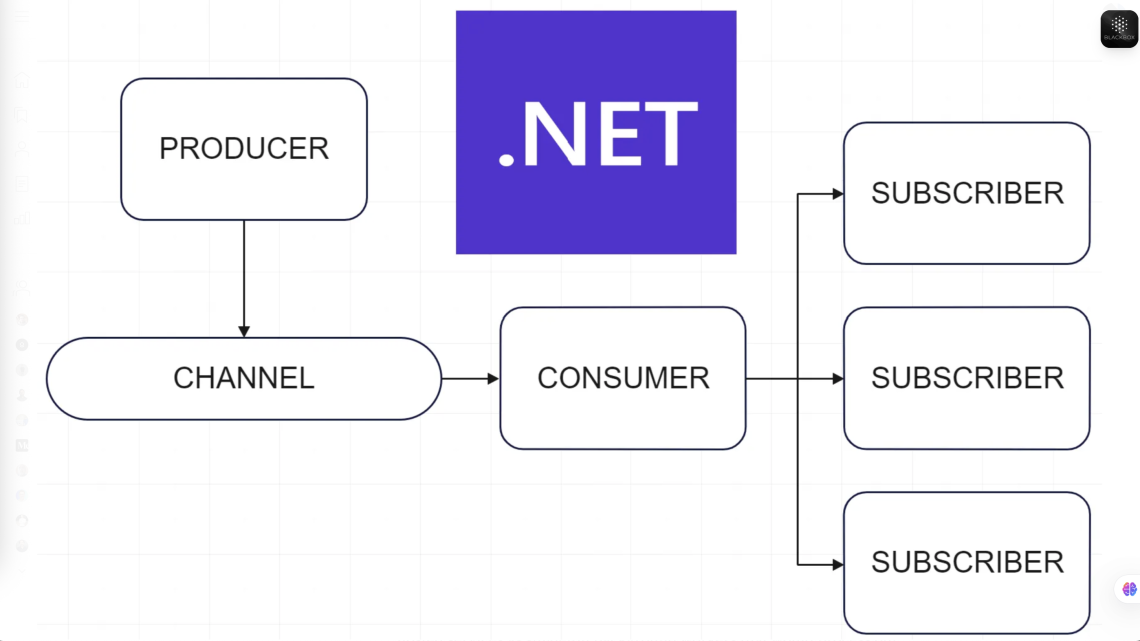
Sử dụng In-Memory Message Bus thay thế cho Masstransit như nào
October 15, 2025Trong các kiến trúc phần mềm, messaging đóng vai trò quan trọng trong việc cho phép các thành phần lỏng lẻo (loosely coupled components) giao tiếp và phối hợp với nhau. Khi yêu cầu hiệu năng cao và độ trễ thấp là tiêu chí hàng đầu, một in-memory message bus là giải pháp đáng cân nhắc. Bài viết này sẽ trình bày cách xây dựng một lightweight in-memory message bus bằng cách sử dụng .NET Channels, đồng thời mô tả cách publish và consume integration events theo hướng bất đồng bộ.
Trước hết, cần lưu ý rằng in-memory message bus không phải là “silver bullet”. Giải pháp này hoạt động rất nhanh vì tất cả dữ liệu đều nằm trong bộ nhớ và hỗ trợ asynchronous communication giữa các module. Tuy nhiên, nhược điểm là nguy cơ mất message nếu tiến trình bị dừng và chỉ hoạt động trong một process duy nhất, không áp dụng cho distributed systems. Vì vậy, use case thực tế phù hợp nhất chính là trong kiến trúc modular monolith, nơi việc trao đổi integration events giữa các module có thể triển khai nội bộ. Nếu sau này cần tách thành microservices, bạn có thể thay thế bằng một distributed message broker.
Để hiện thực, chúng ta cần định nghĩa messaging abstractions. Giao diện IEventBus cung cấp phương thức PublishAsync cho phép publish message, với ràng buộc chỉ nhận vào IIntegrationEvent. Interface này kế thừa từ INotification của MediatR, giúp việc định nghĩa handler trở nên đơn giản hơn. Mỗi IntegrationEvent đều có một định danh duy nhất (Id) để tiện theo dõi.
public interface IEventBus
{
Task PublishAsync<T>(
T integrationEvent,
CancellationToken cancellationToken = default)
where T : class, IIntegrationEvent;
}
using MediatR;
public interface IIntegrationEvent : INotification
{
Guid Id { get; init; }
}
public abstract record IntegrationEvent(Guid Id) : IIntegrationEvent;
Tiếp theo là phần simple in-memory queue using Channels. Namespace System.Threading.Channels cung cấp cấu trúc dữ liệu cho producer/consumer pattern. Bằng cách sử dụng Channel.CreateUnbounded, chúng ta có thể tạo một unbounded channel hỗ trợ nhiều reader và writer. Lớp InMemoryMessageQueue sẽ gói gọn channel này, đồng thời expose ChannelReader và ChannelWriter để publish và consume messages. Service này được đăng ký dưới dạng singleton trong dependency injection.
internal sealed class InMemoryMessageQueue
{
private readonly Channel<IIntegrationEvent> _channel =
Channel.CreateUnbounded<IIntegrationEvent>();
public ChannelReader<IIntegrationEvent> Reader => _channel.Reader;
public ChannelWriter<IIntegrationEvent> Writer => _channel.Writer;
}
builder.Services.AddSingleton<InMemoryMessageQueue>();
Việc implement EventBus trở nên đơn giản khi ta có channel. Lớp EventBus sử dụng InMemoryMessageQueue để ghi các integration events vào channel thông qua Writer. EventBus cũng được đăng ký singleton vì không lưu trạng thái.
internal sealed class EventBus(InMemoryMessageQueue queue) : IEventBus
{
public async Task PublishAsync<T>(
T integrationEvent,
CancellationToken cancellationToken = default)
where T : class, IIntegrationEvent
{
await queue.Writer.WriteAsync(integrationEvent, cancellationToken);
}
}
builder.Services.AddSingleton<IEventBus, EventBus>();
Để consume messages, chúng ta cần một background job. Lớp IntegrationEventProcessorJob kế thừa từ BackgroundService và sử dụng ChannelReader.ReadAllAsync để đọc toàn bộ messages bất đồng bộ. Thông qua IPublisher của MediatR, integration events sẽ được publish đến các handler tương ứng. Việc này được thực hiện trong một scope mới, đảm bảo có thể inject scoped services nếu cần.
internal sealed class IntegrationEventProcessorJob(
InMemoryMessageQueue queue,
IServiceScopeFactory serviceScopeFactory,
ILogger<IntegrationEventProcessorJob> logger)
: BackgroundService
{
protected override async Task ExecuteAsync(CancellationToken stoppingToken)
{
await foreach (IIntegrationEvent integrationEvent in
queue.Reader.ReadAllAsync(stoppingToken))
{
try
{
using IServiceScope scope = serviceScopeFactory.CreateScope();
IPublisher publisher = scope.ServiceProvider
.GetRequiredService<IPublisher>();
await publisher.Publish(integrationEvent, stoppingToken);
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
logger.LogError(
ex,
"Something went wrong! {IntegrationEventId}",
integrationEvent.Id);
}
}
}
}
builder.Services.AddHostedService<IntegrationEventProcessorJob>();
Khi sử dụng, ví dụ trong RegisterUserCommandHandler, sau khi lưu thông tin user vào repository, ta có thể publish một UserRegisteredIntegrationEvent thông qua eventBus.PublishAsync. Message này sau đó được đọc bởi background job và chuyển tới UserRegisteredIntegrationEventHandler, nơi ta implement logic xử lý bất đồng bộ.
internal sealed class RegisterUserCommandHandler(
IUserRepository userRepository,
IEventBus eventBus)
: ICommandHandler<RegisterUserCommand>
{
public async Task<User> Handle(
RegisterUserCommand command,
CancellationToken cancellationToken)
{
// First, register the user.
User user = CreateFromCommand(command);
userRepository.Insert(user);
// Now we can publish the event.
await eventBus.PublishAsync(
new UserRegisteredIntegrationEvent(user.Id),
cancellationToken);
return user;
}
}
internal sealed class UserRegisteredIntegrationEventHandler
: INotificationHandler<UserRegisteredIntegrationEvent>
{
public async Task Handle(
UserRegisteredIntegrationEvent event,
CancellationToken cancellationToken)
{
// Asynchronously handle the event.
}
}
Tuy hệ thống này đã hoạt động, vẫn có thể cải thiện thêm về resilience (thêm retry khi gặp exception), idempotency (tránh xử lý một message nhiều lần) và Dead Letter Queue (lưu trữ các messages không xử lý được để phân tích sau). Đây là các yếu tố quan trọng nếu muốn nâng cấp từ một demo sang giải pháp production-ready.
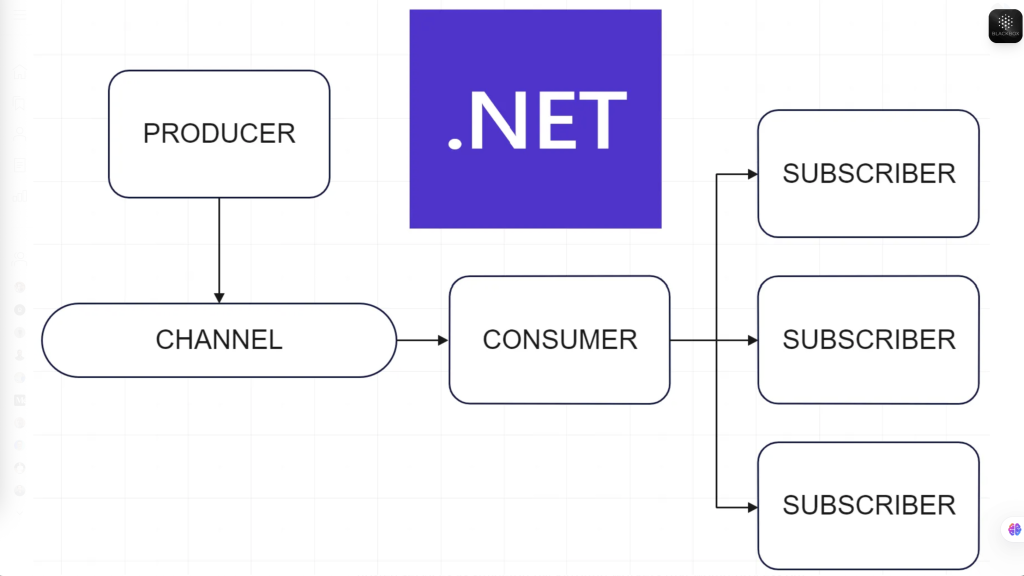
Việc xây dựng một lightweight in-memory message bus using .NET Channels là cách tiếp cận đơn giản, hiệu quả và hiệu năng cao để xử lý integration events trong modular monolith. Tuy nhiên, hãy nhớ rằng giải pháp này chỉ phù hợp trong phạm vi một process. Nếu yêu cầu của bạn hướng tới hệ thống phân tán hoặc cần độ tin cậy cao, hãy cân nhắc sử dụng một real message broker như RabbitMQ, Kafka hoặc Azure Service Bus.
Tham khảo thêm:

